They say the first impression is the last impression and hair has a lot to do with it. How you look is greatly impacted by your hairstyle and how well you wear your hair. Hair loss is the biggest dilemma of today’s world and it affects your overall appearance negatively. Also, it shatters your confidence in the worst way imaginable. Today we will talk about hair loss causes and how you may stop it.
Also, stay tuned for our upcoming article where we will suggest some natural ways to regrow your hair.
Common Hair Loss Causes
Some hair fall daily is normal but if your hair is falling terribly and you see a visible pattern of baldness, something is going on. It could be a traumatic experience or some underlying cause that needs immediate attention.Always take your hair fall seriously.
Some of the common causes of hair fall are:
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics play an important role in determining your hair health. If you have a family history of hair loss, chances are you can also face the issue. However, if hairy genes run in your family, you can enjoy loads of treasure on your body.
Genetic conditions usually affect your roots causing permanent hair loss. One such common genetic condition is Androgenetic Alopecia. It affects hair follicles and causes hair to thin out gradually.
Hormonal Hair Loss
 Our body goes through a lot of hormonal changes. Unnatural fluctuation of hormones can cause hair fall and pattern baldness. In both men and women, testosterone plays a role in the development of hair. However, when testosterone is converted into DHT by the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, it can have detrimental effects on hair follicles.
Our body goes through a lot of hormonal changes. Unnatural fluctuation of hormones can cause hair fall and pattern baldness. In both men and women, testosterone plays a role in the development of hair. However, when testosterone is converted into DHT by the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, it can have detrimental effects on hair follicles.
DHT has a miniaturizing effect on hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time. This process is known as follicular miniaturization. As the follicles become smaller, the hair they produce becomes thinner and shorter. DHT also shortens the growth phase of the hair cycle, leading to a more rapid turnover of hair. This results in a higher number of hairs entering the resting phase (telogen phase) and eventually falling out.
In men, hormonal hair loss often presents as a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, eventually leading to baldness. In women, it can lead to overall thinning of the hair, especially at the crown, without a distinct receding hairline. Also, conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can affect women hair health badly.
Styling Stress Can Cause Hair Loss
 Everything comes with a price and so is beauty. Fashion styling practices involve frequent and aggressive manipulation of the hair, which can contribute to hair loss. Here are some ways in which fashion styling may lead to hair loss:
Everything comes with a price and so is beauty. Fashion styling practices involve frequent and aggressive manipulation of the hair, which can contribute to hair loss. Here are some ways in which fashion styling may lead to hair loss:
- Traction alopecia is a type of hair loss caused by the constant pulling or tension on hair follicles. Tight hairstyles such as braids, ponytails, cornrows, or hair extensions can exert excessive tension on the hair shafts, leading to inflammation and eventual hair loss.
- Excessive use of heat-styling tools like flat irons, curling irons, and blow dryers can cause damage to the hair shaft, making it more prone to breakage. Frequent use of high temperatures can weaken the hair structure, leading to hair loss over time. It’s important to use heat styling tools with caution and incorporate heat-protectant products.
- Harsh chemicals in hair dyes, relaxers, and perms can damage the hair cuticle and weaken the hair shaft. Overlapping chemical treatments or using them too frequently can exacerbate the damage.
- Wearing hats, caps, or headbands that are too tight can cause friction and pressure on the hair follicles. Prolonged use of tight headwear can lead to a condition known as frictional alopecia, where the constant rubbing weakens the hair shaft and causes it to break.
- Brushing the hair too aggressively, especially when they are wet, or using the wrong type of brush can lead to hair breakage and loss. It’s important to use a wide-tooth comb on wet hair and be gentle to avoid unnecessary stress on the hair.
- Glued or sewn-in hair extensions and weaves can pull on the natural hair, causing tension and stress on the follicles. Prolonged use of extensions or weaves without giving the natural hair a break can contribute to traction alopecia and damage the existing hair.
Nutritional Deficiencies And Their Connection To Hair Loss
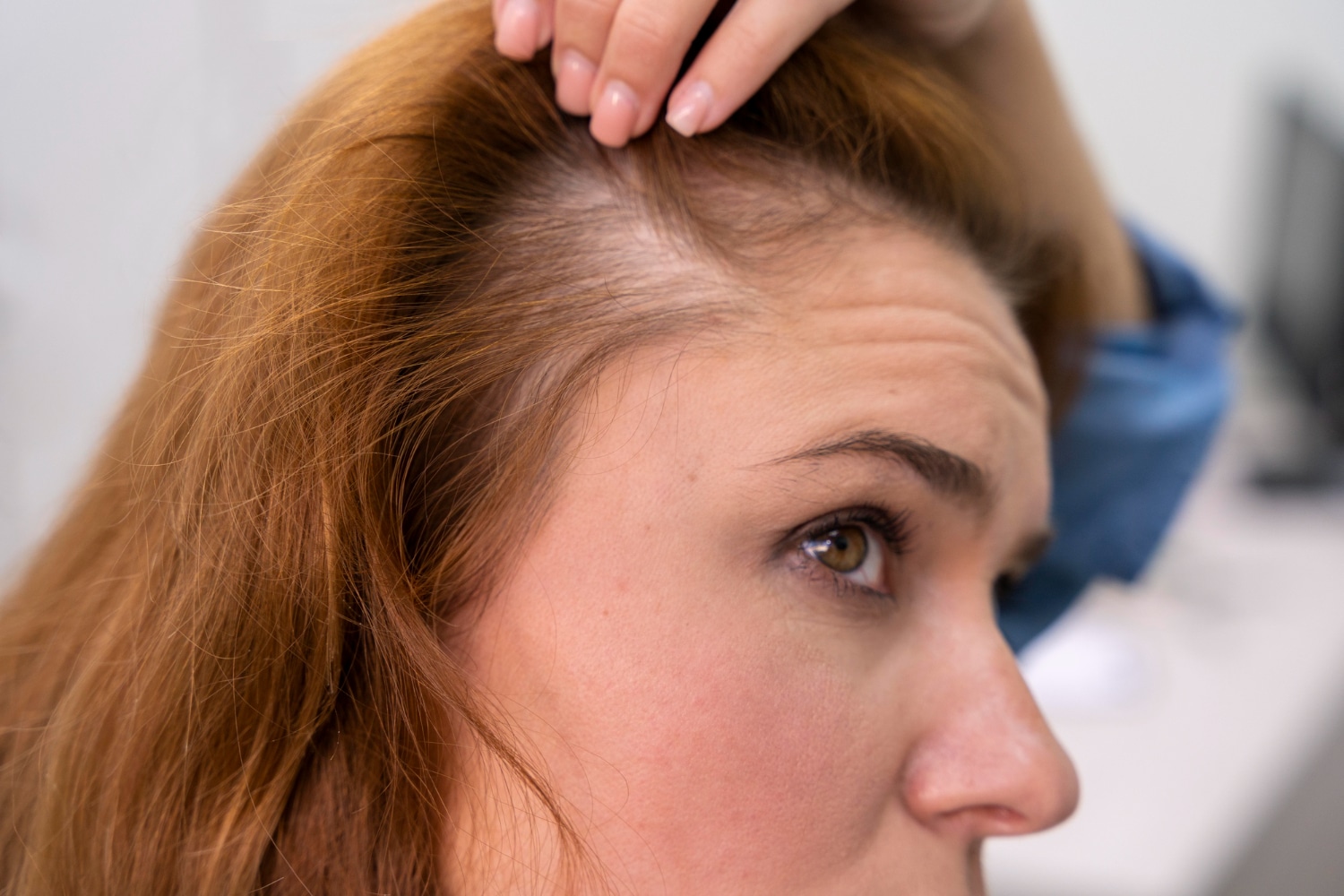 Nutritional deficiencies can play a significant role in hair loss because the hair follicles require a variety of nutrients to grow and remain healthy. When the body lacks essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients, it can negatively impact the hair growth cycle. Here are some key nutritional deficiencies that can contribute to hair loss:
Nutritional deficiencies can play a significant role in hair loss because the hair follicles require a variety of nutrients to grow and remain healthy. When the body lacks essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients, it can negatively impact the hair growth cycle. Here are some key nutritional deficiencies that can contribute to hair loss:
- Insufficient iron levels can lead to anaemia, which has been linked to a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium. In this condition, a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting phase prematurely, leading to increased shedding.
- Vitamin D plays a role in hair follicle cycling. Deficiency may contribute to alopecia, and research suggests that individuals with low levels of vitamin D may be more prone to hair loss.
- Zinc is involved in the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins, essential for hair growth. A deficiency in zinc has been associated with telogen effluvium and alopecia.
- Biotin is often associated with hair and nail health. A deficiency in biotin can lead to hair thinning and loss. However, biotin deficiencies are relatively rare, and supplementation should be done under medical supervision.
- While vitamin A is essential for overall health, excessive intake can lead to hair loss. It’s important to maintain a balance, as both deficiency and excess can negatively impact hair follicles.
- Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to overall scalp health and hair density. A deficiency in these essential fats may lead to dry scalp conditions and increased hair shedding.
- Hair is primarily composed of a protein called keratin. Inadequate protein intake can affect hair structure and growth. Severe protein deficiency may lead to a type of hair loss known as telogen effluvium.
- Vitamin E has antioxidant properties that contribute to a healthy scalp. A deficiency may lead to increased oxidative stress, potentially impacting hair growth.
Stress And Hairfall
Stress triggers the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can affect hormonal balance in the body. Elevated cortisol levels may disrupt the normal hair growth cycle and contribute to hair loss. Hormonal fluctuations can push more hair follicles into the resting phase. Stress can also reduce blood flow to various parts of the body, including the scalp. Inadequate blood flow can compromise the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the hair follicles, affecting their health and contributing to hair shedding.
Also, Chronic stress can suppress the immune system’s normal functioning. In conditions like alopecia areata, where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, stress may exacerbate the autoimmune response, leading to hair loss.
Moreover, stress and anxiety disorders can sometimes manifest as trichotillomania, a condition where individuals compulsively pull out their hair. The act of pulling out hair, often done unconsciously, can lead to significant hair loss over time.
The Effect Of Pollution On Hair Fall
 Air pollution, can contribute to hair loss through various mechanisms. The pollutants present in the air can have detrimental effects on the health of both the scalp and the hair follicles. Here’s how pollution can be linked to hair loss:
Air pollution, can contribute to hair loss through various mechanisms. The pollutants present in the air can have detrimental effects on the health of both the scalp and the hair follicles. Here’s how pollution can be linked to hair loss:
- Air pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and heavy metals, generate free radicals when they come into contact with the skin and hair. Free radicals can cause oxidative stress, leading to damage to the hair follicles and the scalp. This damage, if not adequately addressed, may contribute to hair loss over time.
- Pollutants can irritate the scalp, leading to inflammation. Chronic inflammation of the scalp may compromise the health of hair follicles, disrupt the hair growth cycle, and contribute to conditions like telogen effluvium, where hair sheds prematurely.
- Air pollutants can decrease the oxygen levels in the air and block hair follicles. Inadequate oxygen supply to the hair follicles can impair their function and reduce nutrient delivery, negatively impacting the growth cycle and leading to hair loss.
- Accumulation of pollutants on the scalp and hair can create a layer of toxins. The buildup of toxins can clog hair follicles, disrupt the natural balance of the scalp, and contribute to conditions like folliculitis, potentially leading to hair loss.
- These chemical pollutants in the air, can also weaken the structure of the hair shaft. Weakened hair shafts are more prone to breakage and split ends, which can lead to overall hair thinning and loss.
P:S: This is not a scientific article. It is written with the intent of spreading common knowledge to create awareness about hairfall. Do not use it for research purposes.








